Search engines have evolved from keyword density counters to intent-driven matchmakers. That means you can no longer afford to guess which keywords “might work.” You need to know exactly what people are searching for, and why.
Let’s break down how many types of keywords in SEO actually matter, how each one works, and how to use them to attract traffic that converts, not just clicks.
Why Are Keywords Important in SEO?
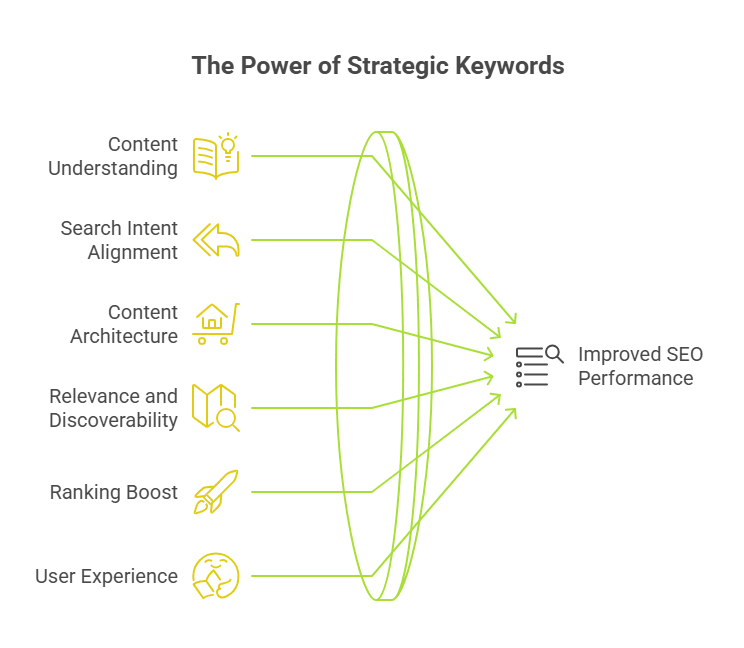
Infographic of Why Are Keywords Important in SEO
Keywords are the connective tissue between search engine algorithms and human queries. When used strategically, they don’t just bring traffic, they bring the right traffic. Here’s how:
1. Keywords Help Search Engines Understand Your Content
Search engines like Google use sophisticated NLP (Natural Language Processing) to parse page content. Keywords, especially when placed in headings, meta tags, alt text, and semantic HTML, act as key signals that clarify the topic and context of your page.
2. Keywords Align Your Content with Search Intent
Modern SEO is intent-driven. Keywords reveal why someone is searching: to learn, compare, or convert. Choosing between informational, commercial, or transactional terms helps ensure your page satisfies the query’s underlying purpose, boosting relevance and ranking potential.
3. Keywords Guide Content Architecture and Internal Linking
Your keyword optimisation strategy shapes more than just content; it influences your site structure. Mapping keywords to content clusters, pillar pages, and subtopics allows for better siloing and internal linking, improving crawlability and PageRank distribution.
4. Keywords Improve Relevance and Discoverability
When your content uses the exact language your audience uses, it’s more likely to rank for that query. Tools like Google Search Console, Ahrefs, or SEMrush can identify high-value keywords where your pages are already gaining impressions, but not yet clicks.
5. Keywords Boost Ranking for Targeted Queries
Using a mix of short-tail, long-tail, and semantic (LSI) keywords improves topical depth. This helps you rank for a broader keyword set (semantic footprint) while hitting those high-intent queries that convert.
6. Keywords Enhance the User Experience
Good keyword usage leads to clearer page titles, structured headings, and focused content, all of which improve readability. When users quickly find what they’re looking for, dwell time increases and bounce rates drop, both positive user signals for SEO.
20 Keyword Types Every SEO Strategy Should Include
Not all keywords are created equal, and neither should your strategy be. This table breaks down every essential keyword type by category, helping you target the right queries at the right stage of the search journey.
| Category | Keyword Type | Purpose |
| Search Intent | Informational | Answer questions, drive awareness |
| Navigational | Find a specific site or brand | |
| Commercial Investigation | Compare options before purchase | |
| Transactional | Drive immediate action or purchase | |
| Length | Short-Tail | Broad topics, high volume, low intent |
| Medium-Tail | Balanced specificity and search traffic | |
| Long-Tail | Niche queries, high intent, low competition | |
| Match Type | Exact Match | Matches the exact query, highly specific |
| Phrase Match | Matches a phrase within a broader query | |
| Broad Match | Flexible matching, wide reach | |
| Negative | Excludes irrelevant or low-intent queries | |
| Role in Content | Primary | Main keyword target for a page |
| Secondary | Supports primary keyword, adds context | |
| LSI / Semantic | Related terms that enhance topical depth | |
| Competitor | Keywords your competitors are ranking for | |
| Targeting Goal | Branded | Includes a brand or product name |
| Generic | Broad industry terms, highly competitive | |
| Market-Specific | Tailored to niche or industry vertical | |
| Review | Used to find feedback before purchase | |
| Customer-Centric | Based on user concerns, goals, or questions |
But here’s the catch: stuffing keywords into your content without understanding their function is like targeting everyone and reaching no one.
If you want to match real search intent and outpace competitors, you need to know what type of keyword you’re working with.
Let’s break them down by purpose.
Types of Keywords by Search Intent
Search engines have become increasingly adept at identifying search intent, the “why” behind a user’s query. Grouping keywords by intent allows you to strategically map them to each stage of the customer journey, creating content that not only ranks but converts.
Here are the four main types of keywords in SEO based on user goal:
1. Informational Keywords
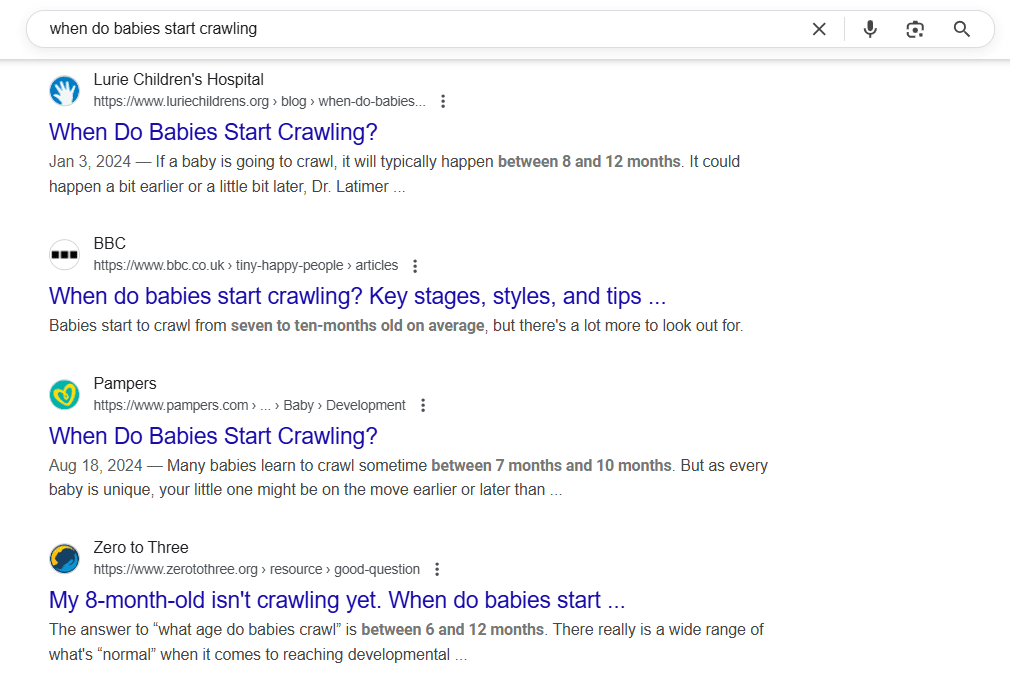
Screenshot of an Informational Keyword
Used during the awareness stage.
Informational keywords indicate that a user is looking to learn something, not buy just yet. These queries typically begin with “how,” “what,” “why,” “when,” or “tips.”
- Example: “when do babies start crawling”, “how to lose weight fast”, “what is SEO”
- Best for: Blog posts, how-to guides, pillar pages, explainer videos
- SEO Tip: Use schema markup (FAQPage or HowTo) to enhance visibility with rich snippets
2. Navigational Keywords
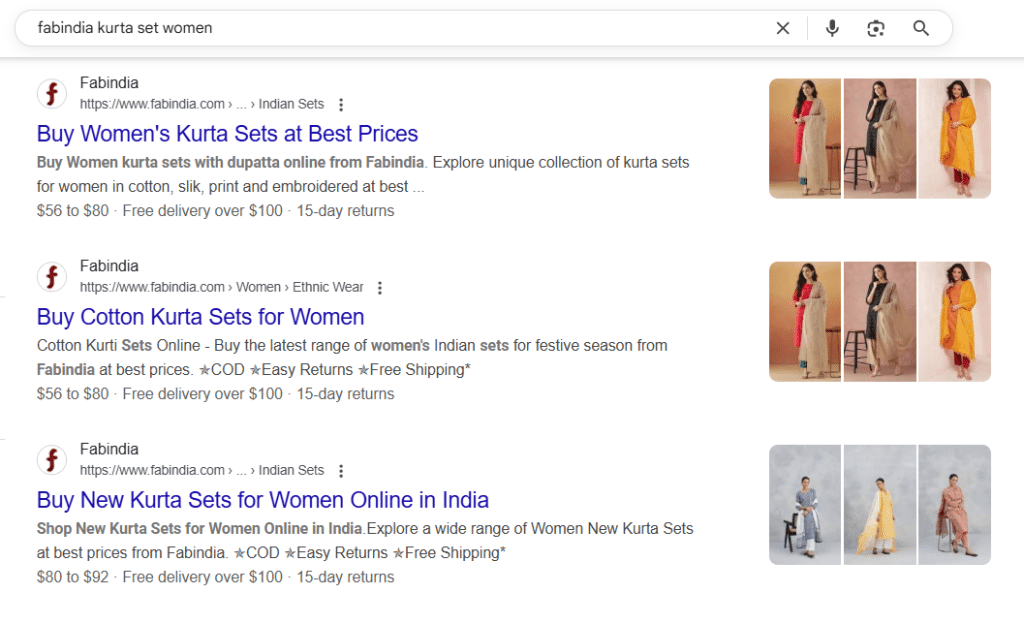
Screenshot of Navigational Keywords
Used to locate a specific brand, product, or website.
These keywords show that the user already knows where they want to go; they just need a shortcut. Navigational intent reflects brand familiarity and typically includes product names, website names, or services.
- Example: “fabindia kurta set women”, “Ahrefs login”
- Best for: Brand landing pages, product pages, homepage optimization
- SEO Tip: Ensure your branded pages are well-optimised and appear as sitelinks for better SERP real estate
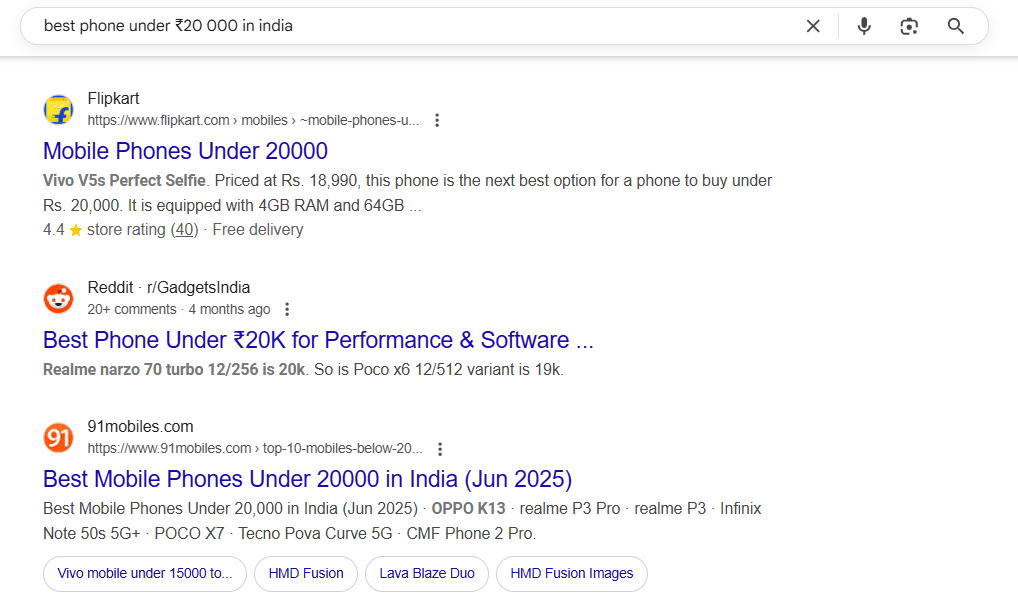
3. Commercial Investigation Keywords
Used during the consideration and comparison phase.
These keywords suggest the user is researching their options before making a purchase. They’re aware of what they want, but need help deciding who or what is best.
- Example: “best phone under ₹20,000 in india”, “Ahrefs vs SEMrush”
- Best for: Comparison articles, product reviews, buyer’s guides
- SEO Tip: Target featured snippet opportunities by formatting content as lists or tables
4. Transactional Keywords
Screenshot of Commercial Investigation Keywords
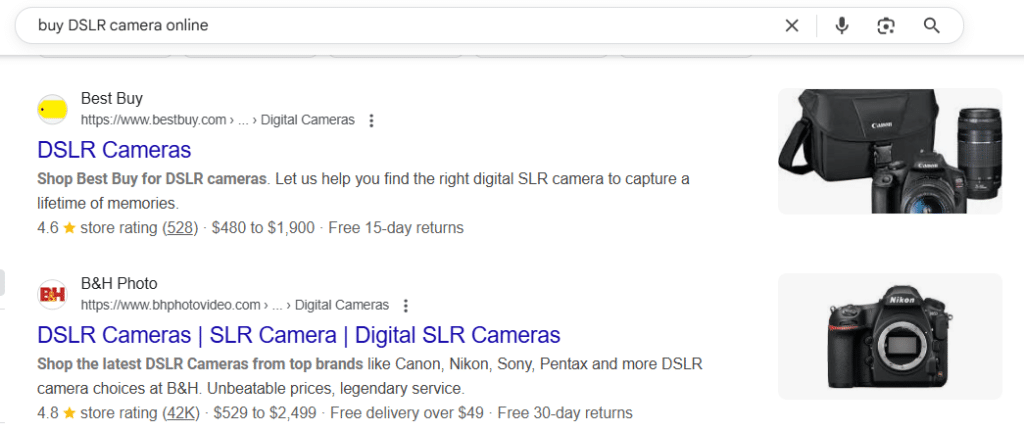
Screenshot of Transactional Keywords
Used at the conversion stage.
These are high-intent queries that indicate the user is ready to take action, buy, subscribe, download, or sign up. They often include words like “buy,” “order,” “discount,” “deal,” or “get now.”
- Example: “buy DSLR camera online”, “order protein powder with free delivery”
- Best for: E-commerce product pages, landing pages, sales funnels
- SEO Tip: Pair these keywords with structured data (Product, Offer, Review) to improve CTR and visibility in shopping results
Writing content around multiple keyword types?
Use our free Word Frequency Counter to spot keyword overuse, ensure balance, and fine-tune your on-page SEO before you hit publish.
👉 Try the Word Frequency Counter →
Types of Keywords by Length
Keyword length isn’t just about word count; it’s a signal of specificity, search volume, competition, and user intent. Grouping keywords by length helps you choose the right mix of visibility and conversion potential across your SEO funnel.
Let’s break down the four most common keyword types by length:
5. Short-Tail Keywords (Head Terms)
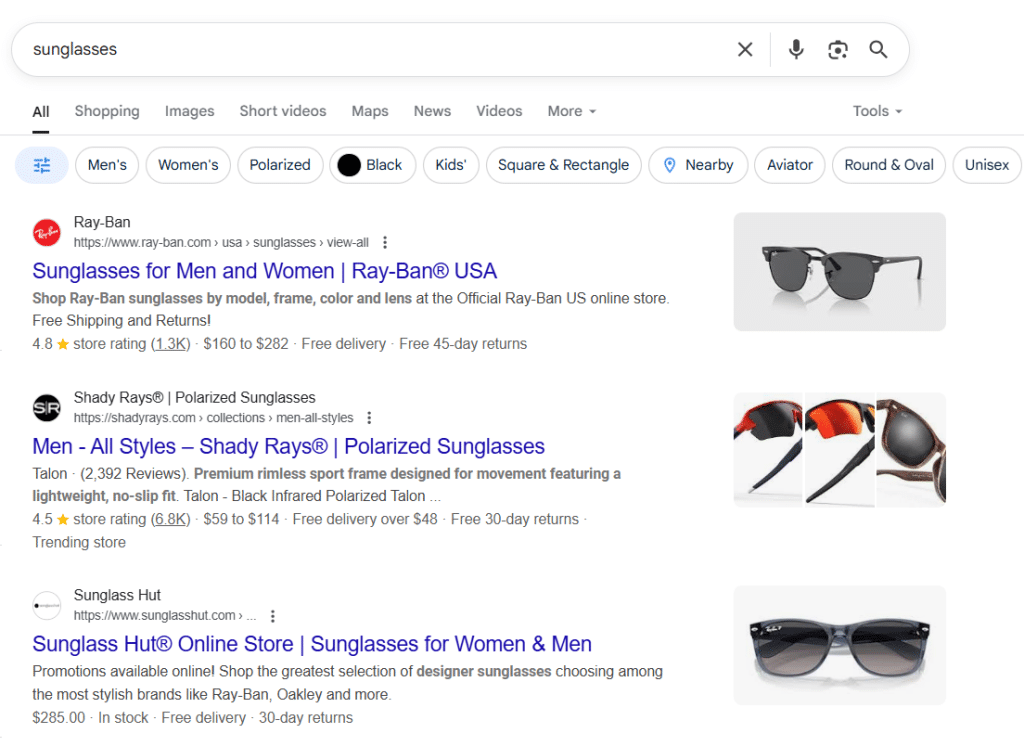
Screenshot of Short Tail Keywords Head Terms
Broad, high-volume, low-intent keywords.
Short-tail keywords are typically 1–2 words long. They generate massive search volume but are extremely competitive and vague in intent.
- Example: “sunglasses”, “SEO”, “marketing”
- Best for: Broad brand awareness, category pages, early-stage content
- SEO Tip: Use short-tail keywords for site architecture and category-level optimisation, but don’t rely on them for conversions; they’re too general.
6. Medium-Tail Keywords
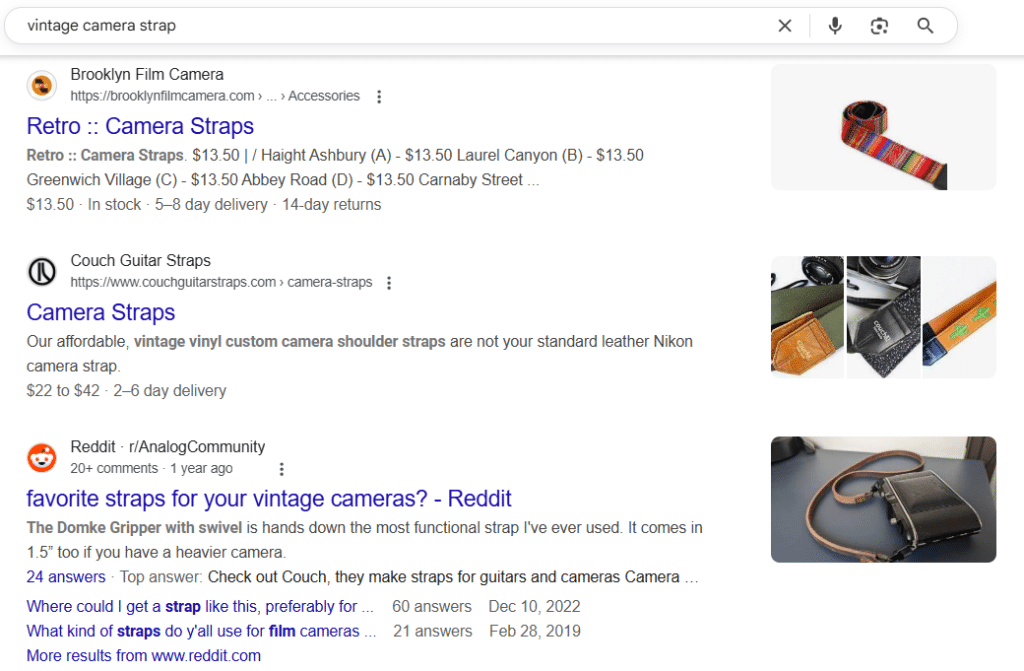
Screenshot of Medium Tail Keywords
Balanced blend of specificity and reach.
Medium-tail keywords usually contain 2–3 words. They offer a sweet spot between volume and precision, making them valuable for both awareness and intent-aligned content.
- Example: “vintage camera strap”, “SEO training course”
- Best for: Topical blog posts, product category pages, mid-funnel targeting
- SEO Tip: Use these to build supporting content clusters around more specific long-tail queries.
7. Long-Tail Keywords
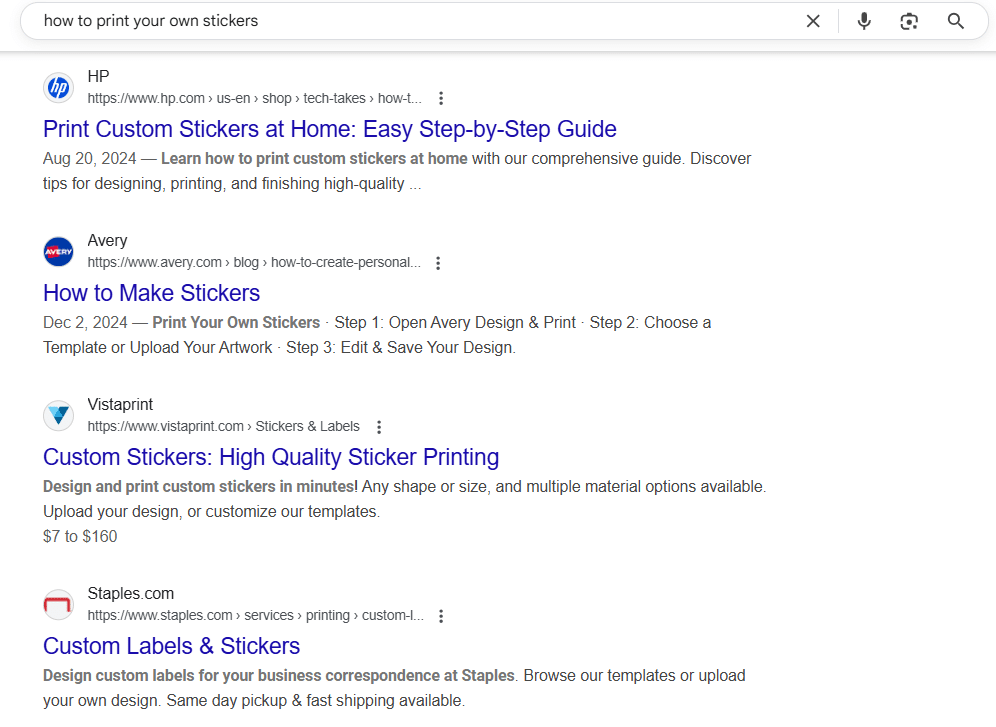
Screenshot of Long Tail Keywords
Highly specific, lower volume, high-converting terms.
Long-tail keywords are 3+ word phrases that target highly specific queries. Though they generate lower traffic individually, they bring in users with strong intent, making them ideal for conversions.
- Example: “how to print your own stickers”
- Best for: Product pages, how-to guides, high-intent blog posts, PPC campaigns
- SEO Tip: Use long-tail keywords to dominate niche segments and capture low-competition SERP real estate. These are especially useful for new sites.
Ranking but not getting results?
Let us audit your keyword strategy and show you which types are driving traffic, but not conversions.
👉 [Book a Free 15-Min SEO Review with Wild Creek]
Types of Keywords by Match Type
Keyword match types determine how closely a search query must align with your keyword for your content or ad to appear. While primarily used in paid search (PPC), these concepts are increasingly relevant in SEO, especially for understanding how Google interprets and surfaces content.
Here are the four core match types every SEO and SEM strategist should know:
8. Exact Match Keywords
Screenshot of Exact Match Keywords
Exact match keywords trigger results only when the search query exactly matches the keyword, or is a close variant (such as singular/plural or reordered terms with the same meaning).
- Example: how to build muscle
- Best for: Highly targeted PPC ads, bottom-of-funnel content
- SEO Insight: In organic SEO, exact match phrases can help anchor key sections (e.g., H1s, product titles), but overuse can lead to keyword stuffing. Use naturally.
9. Phrase Match Keywords
Screenshot of Phrase Match Keywords
These keywords allow your content or ads to appear when a query includes your keyword phrase with additional words before or after.
- Example: “breakfast ideas” may match queries like healthy breakfast or quick breakfast bites.
- Best for: Mid-funnel content, comparison pages, PPC campaigns
- SEO Insight: Phrase match relevance is crucial for blog titles, meta descriptions, and internal link anchor text.
10. Broad Match Keywords
Screenshot of Broad Match Keywords
Broad match allows your content to appear for related or loosely associated terms, including synonyms, misspellings, or conceptually similar phrases.
- Example: A broad match on “cotton pants” might show for “cotton pants and leggings” or “organic joggers for women”
- Best for: Early-stage awareness content or casting a wide net in paid ads
- SEO Insight: Overreliance on broad terms in organic content may reduce topical focus. Use semantic keywords and LSI terms to stay relevant.
11. Negative Keywords
Negative keywords prevent your ads or content from showing up for irrelevant or unqualified traffic. They’re especially important in PPC to reduce wasteful clicks.
- Example: Adding “free” as a negative keyword in paid campaigns for premium products
- Best for: Filtering out traffic with no conversion intent
- SEO Insight: While negative keywords aren’t used in organic SEO directly, understanding search exclusions can help avoid targeting irrelevant queries in your content strategy.
Types of Keywords by Role
For SEO content planning and structure.
Not all keywords serve the same purpose on a page. Some define what the page is about, others support it with topical depth or semantic context. Understanding role-based keyword types helps you create content that is both comprehensive and strategically organised.
12. Primary Keywords (Focus Keywords)
Screenshot of Primary Keywords Focus Keywords
These are the main keywords a page is built around. The entire content structure, headlines, metadata, and internal links should reinforce this keyword.
- Example: take a screenshot on windows
- Best for: H1 tags, page titles, URL slugs
- SEO Insight: Each page should target one clear primary keyword to avoid cannibalisation.
13. Secondary Keywords
These are closely related or supporting terms that add depth to your topic. They help capture variations and expand the content’s semantic footprint.
- Example: For the primary keyword take a screenshot on windows, secondary keywords could include can we screenshot on windows, apps to screenshot on windows, where to save screenshot on windows.
- Best for: Subheadings, body copy, FAQs
- SEO Insight: Use keyword research tools to identify secondary keywords with lower difficulty and complementary intent.
14. LSI Keywords (Latent Semantic Indexing / Semantic Keywords)
These are conceptually related phrases that help search engines understand content context and topic relationships. They’re not synonyms, but thematically linked.
- Example: For weight loss diet, LSI keywords include calorie intake, metabolism, healthy meal plan
- Best for: Improving topical relevance and passage indexing
- SEO Insight: Use LSI keywords to avoid repetition and enhance content quality without over-optimising.
15. Competitor Keywords
These are keywords your competitors are currently ranking for. Analysing them can reveal content gaps or missed opportunities in your own strategy.
- Example: If your competitor ranks for ergonomic gaming chairs under $200, consider creating better content around that query.
- Best for: SEO gap analysis, content repositioning, and backlink strategy.
- SEO Insight: Tools like Ahrefs, SEMrush, or SpyFu can help you track and target these keywords effectively.
Types of Keywords by Targeting Goal
Highly relevant for local, branded, and niche marketing strategies.
These keywords help you connect with specific user segments, purchase stages, or brand-focused queries. They’re essential for driving qualified traffic and improving conversion rates.
16. Branded Keywords
Screenshot of Branded Keywords
These contain your brand or product name and indicate strong brand recall. Users searching these terms are already familiar with your business.
- Example: Apple iPhone 15, Nike Air Max
- Best for: Homepage, product pages, brand campaigns
- SEO Insight: Ensure your site ranks #1 for your branded terms and dominates the first page to protect brand equity.
17. Generic Keywords
Screenshot of Generic Keywords
Broad and non-specific, these represent high-volume, competitive queries often used early in the search process.
- Example: smartphones, laptops
- Best for: Top-of-funnel awareness content
- SEO Insight: These are difficult to rank for without a strong domain authority or comprehensive content hub strategy.
18. Market-Specific Keywords
Screenshot of Market Specific Keywords
These are tailored to niche verticals or categories within your industry. They attract highly targeted users.
- Example: bamboo kitchenware, organic cotton baby clothes
- Best for: Niche blogs, collection pages, influencer content
- SEO Insight: Long-tail, market-specific keywords are ideal for new or lower-authority sites looking to capture underserved queries.
19. Review Keywords
Screenshot of Review Keywords
These indicate that the user is evaluating a product or service and is nearing a decision.
- Example: best SEO tools 2025 reviews
- Best for: Affiliate content, YouTube SEO, blog reviews
- SEO Insight: Use review-rich snippets and structured data to increase visibility and trust signals.
20. Customer-Centric Keywords
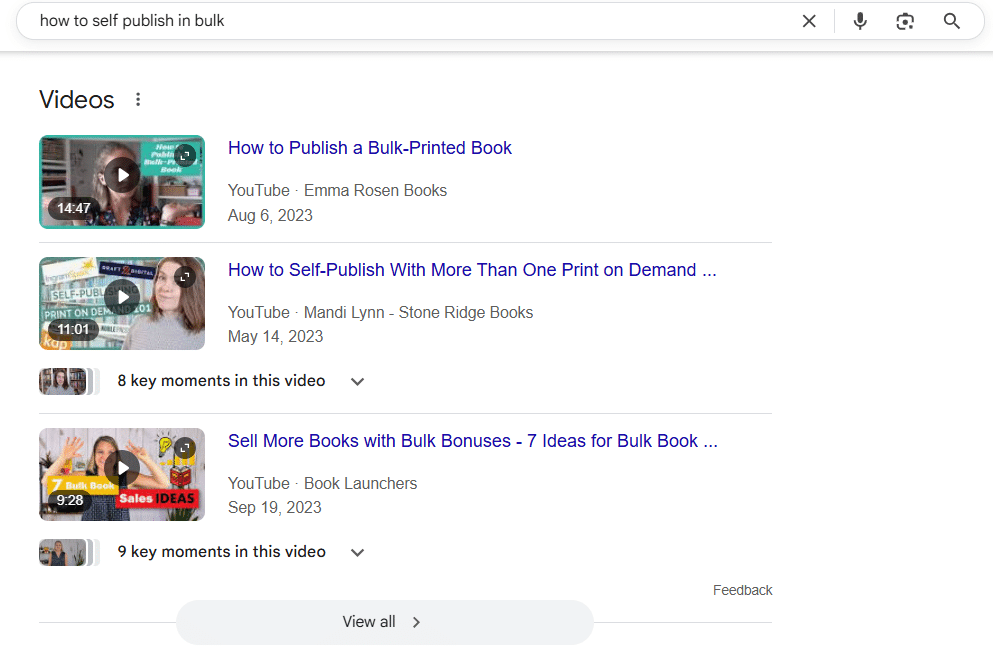
Screenshot of Customer Centric Keywords
These reflect how your audience thinks and speaks, often in the form of problems, goals, or common questions.
- Example: how to self publish in bulk, how to fix slow WiFi at home
- Best for: FAQ sections, blog content, lead-gen pages
- SEO Insight: Extract these keywords from forums, customer surveys, and “People Also Ask” boxes for hyper-relevant content ideas.
How to Find the Right Keyword Types?
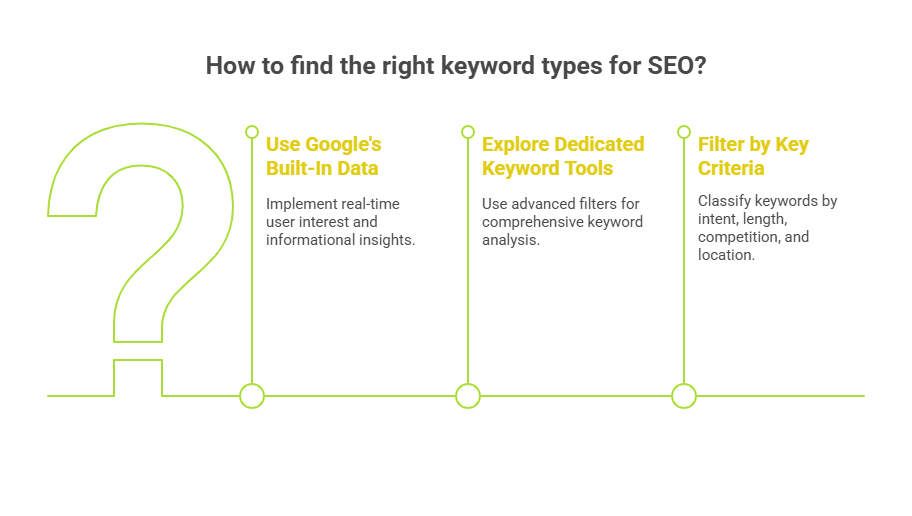
Infographic of How to Find the Right Keyword Types
Knowing the types of keywords in SEO is only half the game. The other half is being able to find and filter the right ones for your content, your audience, and your goals.
Below are essential tools and methods to uncover keyword types based on search behaviour, length, competition, and regional relevance.
1. Use Google’s Built-In Data
Google’s own interface is one of the most underrated keyword research tools.
- Autocomplete (Search Suggestions): Start typing a seed keyword and note the long-tail suggestions that appear; these reflect real-time user interest.
- People Also Ask (PAA): These questions give insight into informational and customer-centric keywords. They’re great for FAQs and blog subheadings.
- Related Searches: Found at the bottom of SERPs, these provide adjacent terms often tied to semantic keywords or alternative intents.
2. Explore Dedicated Keyword Tools
These platforms are built for serious SEO research and offer filters to uncover keyword variations by type.
- Answer the Public: Ideal for finding informational, long-tail, and question-based keywords.
- Ahrefs & SEMrush: Full-suite SEO tools that allow deep filtering by keyword difficulty, intent, search volume, and competitor rankings.
- Ubersuggest: A user-friendly tool that provides long-tail keywords, SERP data, and content suggestions.
3. Filter by Key Criteria
Most tools allow advanced filtering; use this to classify keywords by their purpose and potential.
- By Intent: Look for modifiers like “how,” “buy,” “best,” “near me,” and “vs” to determine if the keyword is informational, transactional, or commercial.
- By Length: Target short-tail for awareness, long-tail for conversions, and mid-tail for a balance.
- By SERP Competition: Choose lower-competition keywords if you have a newer site or limited backlink strength.
- By Location or Language: Local keywords can include region names, language variations, or localised slang (e.g., “trainers” vs. “sneakers”).
You’re Ranking, But Not Selling. Here’s Why.
Getting to page one is only half the battle. If your traffic isn’t converting, the real issue isn’t visibility; it’s intent. Most websites rank for keywords that don’t match what their audience is actually looking for. That’s where Wild Creek Web Studio does things differently.
With over 18 years of experience and a human-first, data-backed approach, we don’t just chase traffic; we align your keyword types with buyer intent, sales goals, and long-term content ROI. Whether it’s mapping out long-tail opportunities, fixing keyword cannibalisation, or building a full-funnel content structure, we deliver SEO that’s designed to convert, not just climb rankings.
Your next sale shouldn’t depend on hope. It should depend on the strategy. Let’s build it.
Conclusion
Whether you’re optimising for a specific website, a product with a strong brand name, or a blog post that needs to pull in organic traffic, understanding the right type of keyword to use can make or break your visibility in search results.
From high search volume short-tail queries to relevant keywords with less competition, every keyword has a role to play in how you attract your target audience and convert potential customers. In the world of digital marketing and content marketing, this isn’t optional; it’s foundational.
Ultimately, keywords are more than just SEO; they’re how you speak your audience’s language. Get that right, and the rankings will follow.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main types of keywords in SEO?
The main types include informational, navigational, commercial, and transactional keywords, each aligned with user intent and different stages of the buyer journey.
How do I choose the right type of keyword?
Match keyword type to your goal: use informational for blog posts, transactional for product pages, and branded or market-specific for loyal or niche audiences. Use tools like Google Trends to spot rising topics, analyse related keywords to broaden reach, and pay attention to search traffic patterns across platforms.
Are long-tail keywords better for SEO?
Yes, long-tail keywords usually face less competition, attract targeted traffic, and convert better, especially for new websites or specific products.
Why are LSI keywords important?
LSI (semantic) keywords help search engines understand your content contextually, improving topic relevance and ranking for related search terms.
How can I find keywords with low competition?
Use tools like Ubersuggest or Ahrefs to find type of keywords seo by low keyword difficulty and focus on specific, intent-rich queries with decent search volume.
