You’ve optimised your content, built backlinks, and nailed internal linking, but your rankings still stall. The problem? Your URLs are working against you.
A cluttered, keywordless, or overly complex URL tells Google nothing, and users even less. On the flip side, a clean, SEO-friendly URL signals relevance, improves crawlability, and can boost both your rankings and click-through rates.
In this guide, we’ll break down exactly why URL structure matters for SEO, the anatomy of a high-performing URL, and the fixes you can apply right now to turn your underperforming pages into search-friendly assets.
What Is an SEO-Friendly URL?
An SEO-friendly URL is short, readable, and clearly signals what a web page is about. It’s optimised for both users and search engines, helping Google understand your content while also increasing the likelihood that users click through from search results.
Instead of strings of IDs or meaningless parameters, these URLs use plain-language keywords that reflect the page’s main topic.
Examples:
| ✅ Good URL Example | ❌ Bad URL Example |
| example.com/seo-tools | example.com/page.php?id=1234 |
| example.com/blog/url-structure-seo | example.com/?cat=12&post=455&ref=home |
A well-structured URL not only improves the crawlability of your site, but it also makes every page easier to navigate, share, and rank.
Why URL Structure Matters for SEO?
Infographic of Why URL Structure Matters for SEO
URL structure isn’t cosmetic, it’s strategic. Search engines treat it as a page-level ranking factor, and it plays a critical role in how your site is interpreted, indexed, and prioritised in search results.
Here’s why it matters:
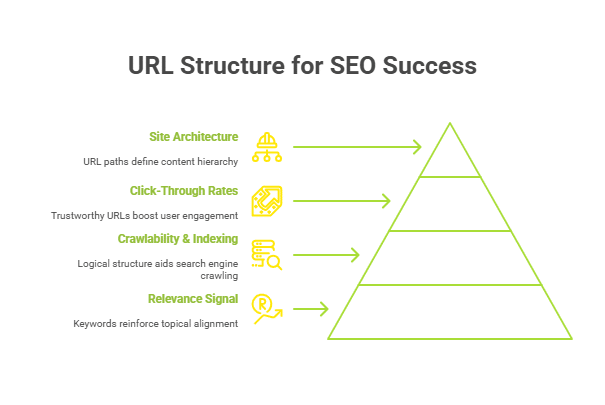
1. It Signals Relevance
Including a keyword in your URL reinforces topical alignment. It’s one of the earliest cues Google gets about your page’s subject.
2. It Enhances Crawlability and Indexing
A consistent, logical folder structure helps search engines crawl deeper and understand how your content is organised, especially on large sites.
3. It Boosts Click-Through Rates
Readable, keyword-based URLs appear more trustworthy and relevant in SERPs, leading to higher CTR from users scanning results quickly.
4. It Supports Site Architecture
URL paths define content hierarchy. A well-structured URL mirrors how your site is organised, aiding both internal linking and user navigation.
In short: your URL is more than a web address. It’s a ranking signal, a UX feature, and a content classifier, all in one line.
What are the 6 SEO URL Best Practices (with Examples)?
Infographic of What are the 6 SEO URL Best Practices
A clean, strategic URL structure can increase crawl efficiency, reinforce content hierarchy, and improve your content’s relevance and click-through rate. Here are key URL optimisation techniques that go beyond the basics, backed by real-world SEO logic and examples.
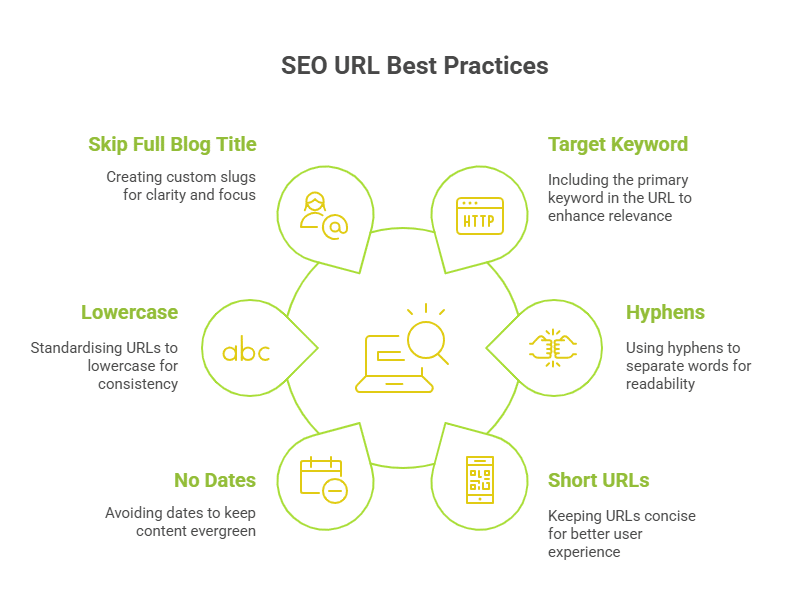
1. Include Your Target Keyword
Screenshot of keyword in URL
Why it matters:
Google uses URLs as a relevance signal, especially when keywords are present. Including the page’s primary keyword helps reinforce the topic and increases your chances of ranking for that exact query.
Technical SEO value:
- Helps Google semantically match the URL with the page content and title tag
- Increases alignment with inbound anchor text (especially when anchors match or partially match the slug)
Example:
- Good: example.com/seo-checklist
- Bad: example.com/article?id=245
Pro tip:
Avoid stuffing multiple keywords. One focused keyword per URL keeps it clean and purposeful.
2. Use Hyphens to Separate Words
Why it matters:
Google explicitly recommends using hyphens over underscores or camelCase to separate words. Hyphens are standard word delimiters in URLs and are treated as spaces by search engines.
Technical SEO value:
- Improves tokenisation (how search engines parse words in the URL)
- Enhances readability and scannability in SERPs
- Prevents misinterpretation of concatenated words
Example:
- Good: example.com/seo-site-audit
- Bad: example.com/seo_site_audit or example.com/seoSiteAudit
3. Keep URLs Short and Clean
Why it matters:
Long URLs are harder to read, prone to truncation in search results, and more likely to contain unnecessary noise like tracking parameters, file extensions, or irrelevant folder names.
Technical SEO value:
- Shorter URLs correlate with better performance in Google rankings (as shown in multiple industry studies, including Ahrefs’)
- Easier to crawl and index
- Higher CTR from users and better shareability across platforms
Example:
- Good: example.com/canonical-tags
- Bad: example.com/seo/article/2025/05/21?id=9432&ref=campaign
Pro tip:
Aim for under 60 characters when possible. Eliminate stop words (the, and, in, for) unless they are part of the search term.
4. Avoid Dates in URLs
Why it matters:
Dates lock your content in time, making updates awkward and hurting CTR if users perceive the content as outdated, even if it’s been refreshed.
Technical SEO value:
- Limits the need for 301 redirects when updating or republishing evergreen content
- Prevents duplicate content issues from publishing “yearly” list posts
- Keeps URLs future-proof and semantically clean
Example:
- Good: example.com/best-seo-tools
- Bad: example.com/best-seo-tools-2023
Real scenario:
If you want to update your 2023 tools list for 2024, you’re either stuck with an outdated URL or you risk splitting link equity across two URLs.
5. Use Lowercase Only
Why it matters:
While most modern servers treat uppercase and lowercase URLs as equivalent, some systems (like Linux-based Apache servers) are case-sensitive, causing crawl errors, broken links, and unnecessary duplicate pages.
Technical SEO value:
- Ensures URL consistency across platforms and environments
- Prevents duplicate content due to capitalisation mismatches
- Keeps internal linking structured and error-free
Example:
- Good: example.com/seo-tools
- Bad: example.com/SEO-Tools or example.com/Seo-Tools
Pro tip:
Standardise lowercase URLs in your CMS and enforce it via .htaccess or redirects where needed.
6. Skip the Full Blog Title in URLs
Why it matters:
Auto-generating slugs based on post titles often results in overly long, diluted URLs that are difficult to read, remember, or update later.
Technical SEO value:
- Shorter slugs increase keyword focus and clarity
- Easier to update content without invalidating the slug
- Improves user trust and click-through behaviour (especially on mobile, where URLs are truncated)
Example:
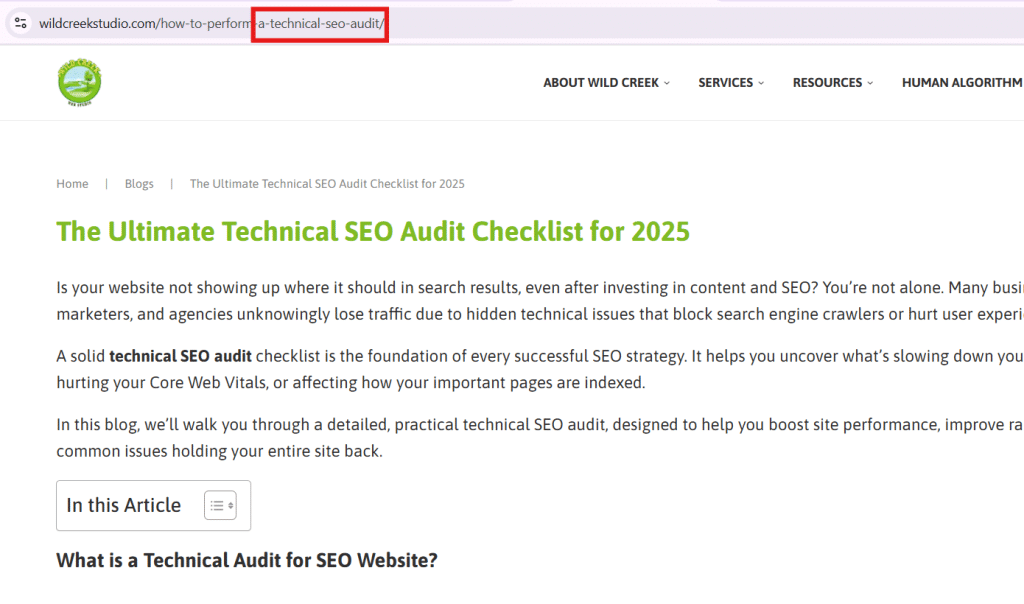
- Blog title: “The Ultimate Guide to Running a Technical SEO Audit in 2025”
- Bad URL: example.com/the-ultimate-guide-to-running-a-technical-seo-audit-in-2025
- Good URL: example.com/technical-seo-audit
Pro tip:
Manually customise each slug to include the seed keyword and nothing more.
How Does URL Structure Impact Crawl Budget?
Googlebot doesn’t crawl your entire site endlessly; it allocates a crawl budget, which is the number of pages it crawls within a given timeframe. If your site has bloated URL structures, such as excessive URL parameters, filter-based variations, or duplicate paths, Google might waste time crawling irrelevant or redundant pages instead of indexing high-value content.
Poor URL hygiene can lead to:
- Index bloat (useless pages getting indexed)
- Delayed updates to important pages
- Missed opportunities for fresh content to rank
For example, an ecommerce site using dynamic filter URLs like:
example.com/shoes?color=red&sort=low-price&page=4
…can generate hundreds of crawlable permutations for the same category, draining crawl resources.
Fix It With:
- Canonical tags: Tell Google which version of a page to prioritise.
- robots.txt exclusions: Block low-value parameter combinations.
- URL parameter handling in Google Search Console: Guide Googlebot on how to treat dynamic strings.
- Clean architecture: Keep primary URLs static, keyword-rich, and minimal.
A logical technical audit checklist ensures your most relevant and updated pages get crawled and ranked efficiently, especially crucial for large websites or high-frequency publishers.
What is the URL Structure for Multilingual or International SEO?
Expanding into global markets? Your URL structure plays a major role in language targeting, localisation, and SEO performance across regions.
There are three main ways to structure international URLs:
| Structure Type | Example URL | SEO Notes |
| Subfolders | example.com/en/ or example.com/fr/ | Easy to manage, shares domain authority |
| Subdomains | en.example.com or fr.example.com | Treated as separate sites by Google |
| ccTLDs | example.in or example.fr | Strong geo-signals, but costly to maintain |
For most brands, subfolders offer the best balance of SEO benefit, management ease, and analytics consistency.
The Role of hreflang Tags
Even with a proper structure, you must use hreflang attributes to:
- Signal the language and regional targeting of each page
- Avoid duplicate content penalties between translated versions
- Improve the chance that users see the correct version in Google search results
Example setup:
- hreflang=”en-us” → example.com/en/
- hreflang=”fr-fr” → example.com/fr/
Keep slug structure consistent across languages for clarity and SEO value, for example, use /en/contact and /fr/contact instead of completely different paths.
Done right, international URL structure helps you reach the right audience in the right language, and improves both SEO visibility and user experience worldwide.
When Your URLs Are Holding You Back, We Help You Fix What Matters
Messy URLs aren’t just bad formatting; they fragment your crawl path, dilute relevance, and quietly sabotage your rankings.
At Wild Creek Web Studio, we’ve spent over 18 years helping brands identify and correct the structural issues most teams overlook. Our audits don’t stop at surface-level fixes. We go deep, mapping URL patterns, cleaning parameter noise, and restructuring folders for clarity, crawlability, and long-term performance.
Our difference? We don’t rely on tools alone. Every audit is led by a strategist who understands both your content architecture and your business priorities.
If your traffic has plateaued and your URL structure hasn’t been reviewed in years, it’s time.
Start with a focused crawl and URL audit, built around your site, not someone else’s checklist.
Conclusion
A well-structured URL may seem like a small detail, but it plays a critical role in search engine optimisation, user experience, and long-term content performance. From using relevant keywords in your slug to keeping URL parameters under control, every decision you make impacts how both users and Google Search interpret your pages.
Whether you’re publishing a new blog post, optimising an old one, or cleaning up your site’s architecture, your uniform resource locator should be more than just a web address; it should reflect clarity, intent, and trust.
Stick to lowercase letters, avoid clutter, and align every slug with your domain name’s purpose. Clean URLs don’t just perform better in search; they’re more likely to be shared, clicked, and remembered across social media and beyond.
Investing in URL structure is one of the simplest yet most overlooked wins in SEO. And now, you know exactly how to do it right.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a simple URL structure and why does it matter?
A simple URL structure helps both users and search engine bots quickly understand the destination page. Clear, keyword-rich slugs reduce confusion and boost visibility in Google search results, contributing to better rankings and a great user experience.
Should I avoid uppercase letters in my URL slugs?
Yes. Uppercase letters in URLs can create duplicate content issues, especially on servers that treat them differently. Stick to lowercase for consistency, especially when using website builders that auto-generate slugs for each particular page.
How does URL structure impact Local SEO and ecommerce sites?
For Local SEO and ecommerce sites, a good URL structure clarifies product or location relevance. URLs like /store/mumbai/shoes help match search queries and guide potential customers to the right destination page faster, improving both rankings and conversion.
Can dynamic URL parameters hurt keyword research efforts?
Yes. Dynamic URL parameters, like strings of characters appended after a question mark, make it harder to associate keywords with a particular page. They also clutter reports, complicating keyword research and diminishing the effectiveness of targeted content strategies.
Is HTTPS with Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) important for URLs?
Absolutely. A secure sockets layer (SSL) ensures data encryption and trust. HTTPS is now a ranking signal in Google search results, and having a secure domain is critical, especially for ecommerce sites or pages that mention a registered trademark of Oracle.
Should I translate URLs for each language version of my site?
Yes-translating URL slugs (e.g., /fr/chaussures for French instead of /fr/shoes) can improve local relevance and click-through rates. Just ensure hreflang tags correctly map each version to avoid duplicate content and maintain search engine clarity.
Can inconsistent URL structures across languages hurt my global SEO?
Absolutely. If your English site uses /en/category/product but the Spanish version uses /producto, it can break content alignment and confuse search engines. Maintain consistent hierarchies to strengthen semantic signals and streamline site maintenance across regions.
