Key Insights
- AI applications outperform humans in structured, data-heavy tasks by offering speed, scale, and precision, but they lack adaptability, ethics, and emotional depth.
- Human intelligence excels in ambiguity, creativity, empathy, and ethical decision making, making it indispensable for guiding technology.
- Research shows AI-only teams perform better in structured contexts, while human-AI collaboration thrives in creative and strategic work.
- The real risk is not AI surpassing humans, but humans outsourcing judgment and failing to think critically.
- True leadership in the AI era means leading with vision, prioritizing ethics, and creating space for human creativity.
- The “Human Algorithm” blends machine efficiency with human judgment, helping leaders think better, not just faster.
- Wild Creek Studio champions this philosophy, guiding organizations to combine AI and human wisdom for purposeful, confident growth.
Why do we keep imagining a showdown between AI and the human brain?
Every headline frames it as a rivalry, as if machines and humans are locked in a battle for dominance. It is a compelling story, but also a misleading one.
When we measure intelligence only by speed, scale, and efficiency, AI seems unstoppable. Yet in chasing this race, we risk overlooking the very qualities that define human intellect: intuition, empathy, creativity, and ethical judgment. The danger is not that AI will outthink us; it is that we will stop thinking for ourselves.
This blog takes you beyond the familiar AI versus human brain debate. Through Wild Creek Studio’s Human Algorithm philosophy, we will explore why it is not about choosing between human and machine, but about combining the best of both.
Human Brain vs Artificial Intelligence: Where Does AI Win the Race?
Illustration of a human brain racing against AI robot on a track
It is easy to think of AI as a passing trend or just another tool. However, that view underestimates its existing edge. In fields driven by data analysis, scale, and precision, AI does not merely compete with humans; it surpasses them.
Research from Cambridge Judge Business School illustrates this clearly. In a simulation of the automobile industry, AI models outperformed human executives in product design, supply chain optimization, and market response.
Even untuned generative models, when prompted well, produced fresh strategic ideas. AI was not simply following instructions. It was shaping strategy.
For leaders, the takeaway is straightforward. In contexts where decisions rely on structured data, such as forecasting demand, detecting disease, or modelling financial risk, AI consistently delivers better results than humans.
Not because it is smarter, but because it works without fatigue, without inconsistency, and with relentless focus.
Powered by machine learning, intelligent machines utilize computational power to tackle complex problems that require logical reasoning and swift task completion.
Yet this advantage has limits. AI is only as good as the data it learns from. If the input is biased or incomplete, the output will carry those flaws forward.
It is no longer a question of whether AI outperforms the human brain, as it already does in many areas. The challenge is to harness that power without compromising human responsibility.
This is where the human algorithm makes a difference. AI brings speed and efficiency. Humans bring discernment and judgment.
Where Does the Human Brain Still Hold Irreplaceable Ground?
Illustration showing a human hand shaking a robot arm beside a brain
AI performs well when tasks are structured, data is clean, and past patterns hold. But change, ambiguity, and emotional nuance expose its limits.
According to a 2024 meta-analysis published in the National Library of Medicine, which reviewed 106 experiments and 370 effect sizes, human and AI teams often underperformed compared to AI alone in structured decision-making tasks.
Yet, for creative tasks such as generating content, imagery, or summarizing social interactions among platforms, human-AI combinations showed significant gains over human-only teams. The findings highlight that humans add the refinement, emotional depth, and context that machines cannot sustain.
That balance is why human cognition remains indispensable in guiding technology, and it is especially clear in content creation, where AI tools for content writing enhance efficiency but still rely on human judgment to deliver quality results.
Is AI Really Outthinking Us, Or Are We Simply Thinking Less?
Illustration of a glowing human brain lighting paths with robot in dark
While the connection between artificial intelligence and human brain activities is often overstated, machines only replicate patterns, not consciousness. They lack the emotional and ethical grounding that defines human decision-making.
As Sundar Pichai, CEO of Google, said: “The future of AI is not about replacing humans, it’s about augmenting human capabilities.”
This is the perspective leaders must adopt. AI can amplify what we do, but it cannot decide why we do it or whether we should.
The danger comes when leaders treat machine outputs as unquestionable truths. Algorithms reflect the data they are trained on, along with their biases and blind spots. Accepting them uncritically means outsourcing judgment. Progress has never come from blind acceptance.
True leadership requires slowing down when technology tempts us to rush. It means asking not just “What did the model predict?” but “Why does this matter and what might it miss?”
The future will not be defined by whether AI mimics human brain processes. It will be determined by whether we continue to think deeply enough to guide them.
A good starting point is learning how to master prompt engineering, a skill that shows how human intent can shape AI outcomes.
How Can the Human Algorithm Help Us Think Better, Not Just Faster?
Illustration showing a robot head in puzzle with brain completing final piece
The real opportunity in the age of AI is not about building faster systems; it’s about creating smarter ones. The human algorithm offers that shift.
AI brings the scale and speed. Humans bring judgment, empathy, and strategy. Alone, each is incomplete. Together, they create clarity and have a lasting impact. Algorithms can process vast amounts of data, but only people can ask the questions that matter and make choices that endure.
For leaders, this is not a choice between human and machine. It is about knowing when to let AI optimize and when to step in with a human perspective. Marketing campaigns, strategic pivots, and cultural decisions cannot be left to models. They demand human vision.
As Karim Lakhani said, “AI will not replace humans, but humans with AI will replace humans without AI.” That is the essence of the human algorithm. It does not remove human thinking. It elevates it.
The leaders who embrace this approach will not just keep pace with technology. They will shape the future of business by thinking better, not faster.
What Does True Leadership Look Like in the Age of AI?
True leadership in the AI era is not about knowing every tool. It is about setting the compass for how technology is used. Leaders who thrive will be the ones who bring human clarity to machine efficiency.
This means three things:
- Leading with vision. AI can generate insights, but it cannot decide which direction aligns with long-term purpose. Leaders must define the “why” before machines help with the “how.”
- Making ethics non-negotiable. Algorithms optimize for outcomes, not values. Leaders must ensure decisions are not only profitable but also fair, transparent, and responsible.
- Creating space for human creativity. While AI can accelerate analysis, innovation depends on human imagination and emotional intelligence. Leaders must cultivate cultures where people feel empowered to challenge, refine, and go beyond what the data suggests.
The leaders who succeed in this new era will not be the fastest adopters of AI. They will be the ones who use it as a partner while keeping judgment, empathy, and responsibility at the center of every decision.
And they will be the ones who help their teams future-proof their careers in the age of artificial intelligence.
How Can AI Shape the Small Decisions We Make Every Day?
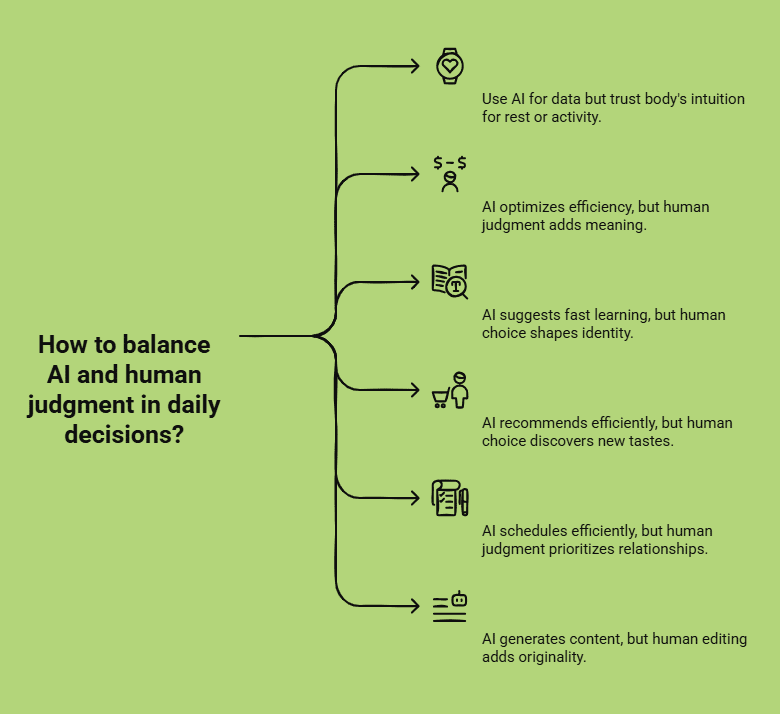
Infographic of how to balance AI and human judgment in daily decisions
Balancing AI and human judgment is not just a leadership question. It shows up in the small, ordinary choices you make every day. The challenge is not whether AI can help, but how to use it without surrendering your own judgment.
Here are some examples where the Human Algorithm comes alive outside the boardroom:
1. Deciding What’s Healthy for You
Your smartwatch may tell you that you slept only five hours and should hit 10,000 steps today. That data is useful, but it is not the whole picture. Maybe you need rest more than a run. AI can show you the numbers, but your body tells you the truth.
2. Spending Money With Purpose
A budgeting app might suggest cutting down on “non-essential” spending. But is that weekend art class non-essential, or is it the thing that keeps you inspired for the rest of the week? AI optimizes for efficiency; only you can optimize for meaning.
3. Learning in a World of Infinite Content
AI can summarize books, draft study notes, or map a learning path in seconds. Yet the decision is not what you can learn fastest, but what is worth learning deeply. That choice shapes who you become, and no algorithm can make it for you.
4. Buying Beyond the Algorithm
Online platforms feed you recommendations based on your clicks. It is efficient, but also narrow. If you only buy what AI serves up, you stop discovering new tastes, styles, or ideas. Sometimes the best choice is to step outside the feed and be surprised.
5. Protecting Your Time and Attention
AI schedulers can fill your calendar with “urgent” tasks. But they cannot tell you that dinner with a friend matters more than another email. Efficiency is useful, but attention is precious, and deciding where to spend it is a human act.
6. Creating Work That Feels Like Yours
Generative AI can draft copy, design slides, or suggest campaign ideas. But left unedited, it is just output. The moment you add your voice, your story, your judgment, it becomes something original. That is the difference between content and connection.
The smartest use of AI in daily life is not about speed or shortcuts. It is about letting machines handle the data while you hold onto direction. When you ask not just “What did AI suggest?” but “Why does this matter to me?” you turn technology into a partner rather than a crutch.
How Is Wild Creek Studio Shaping The Future With The Human Algorithm?
While many businesses rush to automate, Wild Creek Studio asks a different question: how can AI serve human judgment rather than replace it? That question is at the heart of the Human Algorithm, our framework for helping leaders move beyond tools and trends.
At our first Human Algorithm event at IIT Madras Research Park, more than 100 founders, marketers, and decision-makers came together to explore what leadership looks like in an AI-first world. The focus was not on dashboards or hacks. It was on clarity, trust, and strategies that last.
For us, the Human Algorithm is not a campaign. It is a movement. By combining machine intelligence with human wisdom, we are helping leaders shape businesses that grow with purpose and confidence.
If you want to be part of this journey, Connect with Wild Creek Studio and discover how the human algorithm can help your organization think better, not just faster.
Final Thoughts
AI will keep getting faster. Data will keep getting sharper. But leadership is not defined by what machines achieve. It is defined by the choices humans make with them.
The Human Algorithm is an invitation to lead differently. Pause when others rush. Ask the harder questions. Bring judgment, empathy, and imagination into every decision. The leaders who dare to think better, not just faster, will be the ones who shape the future.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can AI make better decisions than humans in all situations?
No. AI excels at data-driven tasks, but humans outperform in ambiguity, ethics, and unpredictable events. Machines process new information logically, while humans apply intuition and context, essential for complex, real-world decisions.
How does human creativity compare to AI creativity?
Generative AI can remix data into creative outputs, but often lacks emotional depth. Human creativity, driven by cognitive processes and diverse forms of intelligence, thrives on originality, refinement, and meaning, areas where artificial systems fall short.
What challenges does AI face when making complex decisions?
AI, rooted in computer science and deep learning, struggles when new or disruptive events arise. Its use of AI depends on historical data, making neural networks less reliable than humans, who can adapt with foresight and intuition.
How do neural networks in AI compare to neurons in our brain?
Neural networks in computer systems mimic brain-like connections but lack true cognitive abilities. Unlike human neurons, which enable complex cognitive processes, AI networks only perform pattern recognition and information processing for specific tasks without intuition or meaning.
Can artificial intelligence ever match or surpass the capabilities of the human brain?
AI powered by machine learning, artificial neural networks, and large language models excels at complex tasks and data-driven problem solving. Yet it lacks adaptability, creativity, and ethical grounding. Unlike AI agents, real brains integrate cognitive functions and diverse intelligences seamlessly.
Is AI as “real” as the human brain?
No. AI systems simulate limited forms of intelligence through algorithms, but they lack consciousness and working memory. The human brain, powered by the nervous system, adapts in different ways, blending emotion, common sense, and lived experience.
What are the energy requirements of AI compared to the human brain?
AI systems demand far more computational power and energy consumption than the human brain. While the brain performs complex tasks with remarkably less energy, AI relies on data centers and hardware to handle cognitive tasks efficiently.
How do brain-machine interfaces aim to synchronize AI and human brain functions?
Brain-machine interfaces connect neural activity and synaptic connections with artificial neural networks and large language models, translating human language into signals that machines process. This enables AI agents to collaborate with people, improving decision-making and extending cognitive capacities effectively.
Does AI work like the human brain?
No. While AI mimics certain brain functions, the difference between AI and the human brain is significant. AI processes data and patterns, while the human brain integrates intuition, creativity, memory, and emotions, enabling more profound understanding and adaptive decision-making.
What is the difference between AI and human intelligence?
The difference between the human brain and artificial intelligence lies in adaptability and depth. AI excels at data-driven tasks, while humans bring intuition, creativity, and ethics. Artificial intelligence and human brain complement each other but are not interchangeable.
